
carat weight
Carat defines the weight of a diamond. A carat is equal to 0.2 grams and is divided into 100 points. A so-called half-carat weighs 0.1 grams and is also referred to as 50 points. Basically, carat weights under 1 carat are referred to as “points”: for example, a 75 point for a stone with 0.75 carat . If it is one carat or more, it is called a “carat”, for example a 1.5 carat .
Learn more about Karat in the official GIA video (currently only available in English).
Choosing the right carat size: Try it!
To give you a better idea of the different carat sizes, we have developed the tool below for you. This will give you a feel for the relationships and make it easier for you to choose the diamond that is right for you. At the bottom left you can choose between the views “Hand with diamond ring” and “Ring setting with diamond”.
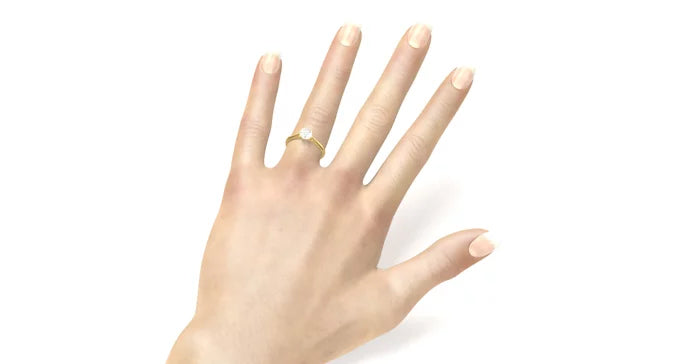
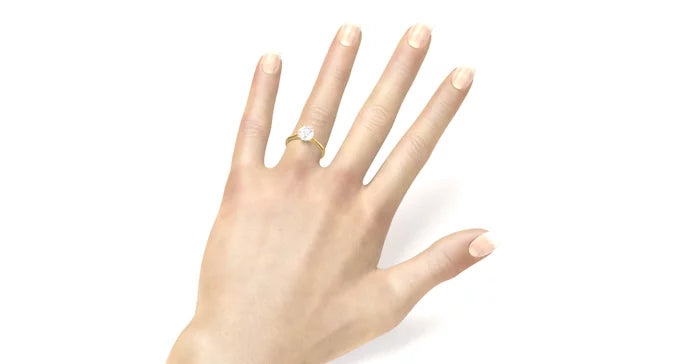
Hand with diamond ring
The hand pictured is wearing a ring, underneath you can see different carat sizes. By clicking on the sizes, the diamond on the ring finger also changes. Find out which size suits your taste.
Ring setting with diamond
So that you can see in detail how different a diamond ring with different carat sizes can look, simply click on the ring setting. Below the graphic the different carat sizes appear again for selection. You will see that the same ring looks completely different with a 0.25 carat diamond than with a 2.00 carat diamond.
The rings in our shop are usually shown with a 1 carat.
Our diamond rings











- 0.25
- 0.50
- 0.75
- 1.00
- 1.25
- 1.50
- 2.00
How big does the diamond appear?
The carat weight does not, as is often assumed, provide direct information about the size of a diamond. Two diamonds with the same carat weight may appear different sizes. Only the combination of carat weight, table, depth and cut grade provides information about the size of the diamond.
Table: The table represents the visible area of the diamond when viewed from above. This is the most common view of a set diamond. The larger the diameter of the table, the larger the diamond appears (otherwise the diamond criteria are the same).
Depth: A particularly deep stone usually appears smaller than a slightly shallower one. For deep stones, a large proportion of the weight is in the lower part of the diamond. This is hidden when viewed from above.
Cut: The higher the degree of cut, the more incident light emerges through the table, and the more beautifully and intensely the diamond sparkles and shines. And the larger the diamond appears to the human eye. Stones with a lower cut grade always appear smaller than stones with a higher cut grade, even with the same diameter of the table and the same number of carats. It is possible for a stone with a small carat weight and smaller table diameter to appear larger due to its higher cut grade than a larger stone with a lower cut grade. Yorxs recommends that you do not compromise on the three cut criteria available (degree of cut, symmetry, polish) for the brilliant cut and the two cut criteria (symmetry, polish) for the other types of cut. Nature gave us the diamond deposits on our planet Earth. The cut is the human part of a finished diamond and determines the appearance of how perfectly a diamond reflects light within the natural conditions.
Carat - weight and size of the diamond
Although diamond size is not determined solely by carat weight, it is an important factor in determining diamond size. For set diamonds - especially brilliant-cut diamonds (i.e. round diamonds) - you can also measure the diamond and estimate the number of carats using the parameters.
To give you a feel for the size of different diamond shapes based on carat weight, Yorxs provides you with the following PDF.
Open PDFHow do I determine the carat weight that is right for me?
This is the question most people ask themselves when buying a diamond. Unfortunately, there is no universal answer. The choice of carat weight depends on the following factors:
Taste: Do you value the quality and fire of the stone more or its size? The answer to this question forms the basis for choosing the carat weight.
Budget: Since the price of a diamond is most influenced by its carat weight, budget plays a crucial role in the choice.
Setting: Setting a diamond can make the gemstone appear larger than it actually is. In a halo setting, for example, the main stone appears up to 0.5 carat larger than it is due to the small diamonds surrounding it.
Shape: The shape of a diamond can make a stone appear larger. Navette or pear diamonds, for example, often appear larger than a brilliant for the same carat weight.
The wearer: When choosing the carat weight, the wearer of the diamond should be considered. For rings, you should choose the carat weight depending on the size of your hand. The following applies: the narrower the fingers of the hand wearing it, the larger the diamond appears.
The value of a diamond & the carat number
The carat weight is the criterion that has the greatest influence on the value of a diamond. The heavier a diamond, i.e. the more carats, the higher the price. Larger diamonds are rarer and more sought after than small diamonds. The price of diamonds therefore does not rise proportionally with its weight, but exponentially. This means that a one-carat diamond does not cost twice as much as a half-carat diamond, but rather several times as much (with otherwise the same quality). As a result, the price of a large diamond is more expensive not only due to the higher weight, but also due to a higher price per carat. So not only does the diamond become more expensive because it is heavier, but the price per carat of a diamond also increases with its weight.
The prices per carat or per fraction of a carat are the same for brilliants with otherwise the same characteristics such as color, cut grade, fluorescence, etc. within the following ranges:
| 0.23 - 0.29 ct | 0.30 - 0.39 ct | 0.40 - 0.49 ct | 0.50 - 0.69 ct | 0.70 - 0.89 ct |
| 0.90 - 0.99 ct | 1.00 - 1.24 ct | 1.25 - 1.49 ct | 1.50 - 1.99 ct | 2.00 - 2.99 ct |
| 3.00 - 3.99 ct | 4.00 - 4.99 ct | 5.00 - 5.99 ct | Etc … | 10.00 - 10.99 ct |
Background to carat weight
The term carat comes from the Greek word “keration” and the Arabic term “qirat”. Both expressions mean “pod of the carob tree.” Long ago, the plant seed was used as a weight to weigh gold and precious stones. It was long thought that the weight of the seed was unusually uniform. Researchers refuted this assumption. In 1907, carat was finally established as the official metric measurement for gemstones. Six years later, the US accepted the measure and Europe and Britain followed suit a year later. Today the standardized measurement is used worldwide for diamonds and gemstones.
Our recommendation for carats
With diamonds there are “magic thresholds” at which price jumps occur. A 1 carat diamond, for example, costs significantly more than a 0.95 carat diamond, although the difference in size is hardly visible. You can sometimes save money by purchasing a diamond that is only slightly lighter in weight. 0.5 carat, 1 carat, 1.5 carat and 2 carat are carat weights where price jumps are most noticeable.
Find diamonds by carat
Our team is there for you!
Dear website visitors and customers, do you have any questions, requests or suggestions? Please call us (Tel.: 0800 8880770 ).
You can also reach us at our email address service@yorxs.de .
We are available for you from Monday to Friday from 10 a.m. to 6 p.m. and Saturday from 10 a.m. to 3 p.m. Talk to us - we are always happy to help you.